Mechanism of cell slippage during mitotic arrest a Rapid degradation Biology Diagrams Recovery of TRF2 (TERF2) and other shelterin components by Flag-APEX2-TRF1 modestly decreased in abundance during mitotic arrest (Supplementary Fig. 1e), consistent with prior observations of

Here I discuss how the same mechanism--namely, inhibition of transcription during mitosis--can explain (1) apoptosis during mitotic arrest, (2) mitotic slippage, (3) G1 arrest after mitotic slippage and (4) secondary apoptosis after mitotic slippage. In fact, during mitotic arrest transcription is a …

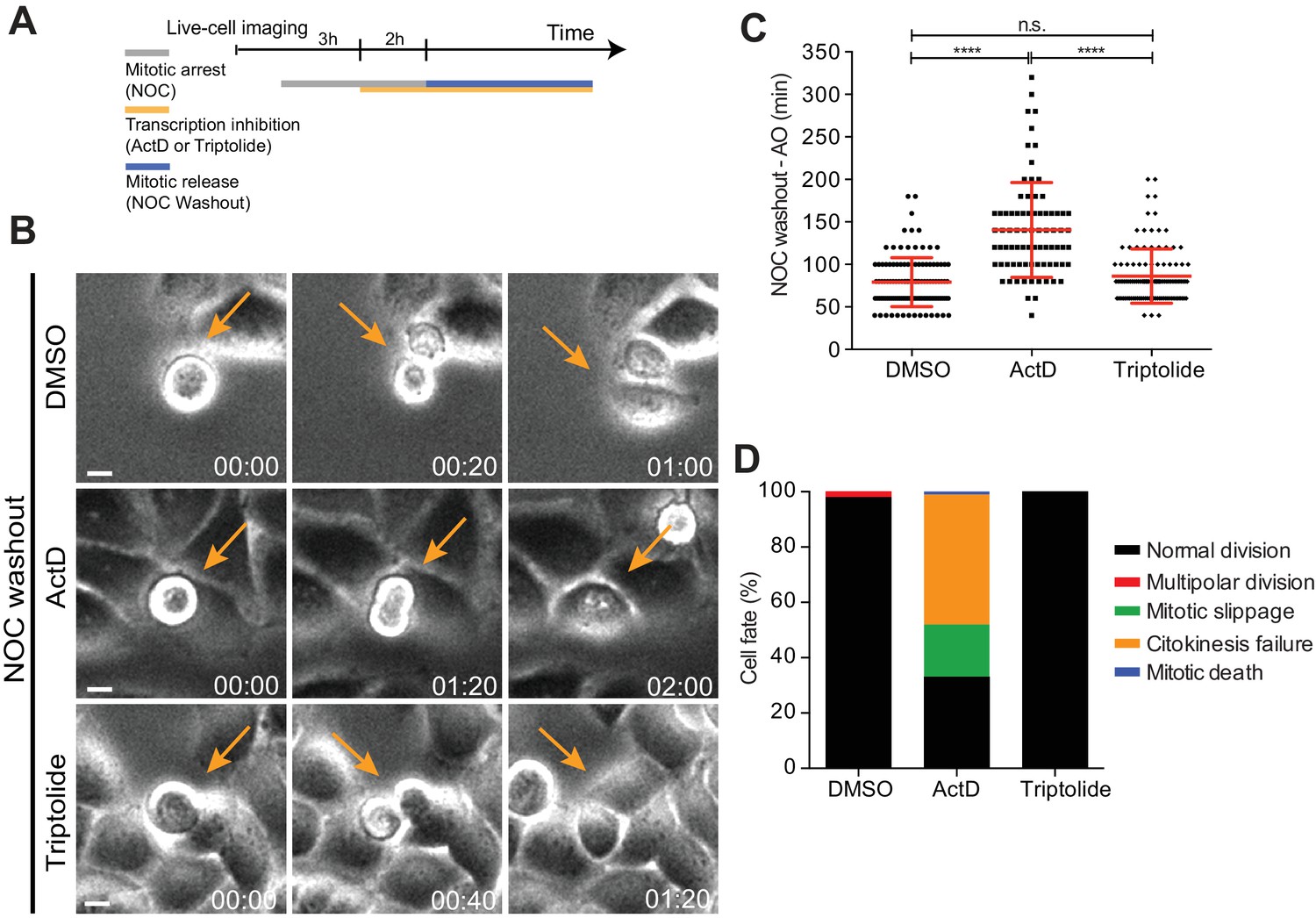
lncreased risk of slippage upon disengagement of the mitotic checkpoint ... Biology Diagrams
Here, using a tunable system of chromosome mis-segregation, we show that mitotic errors trigger nuclear deformation, nuclear softening, and lamin and heterochromatin alterations, leading to rapid Whether recovery is a passive process in the absence of the checkpoint-inducing signals or requires active participation of specific effectors has not been explored extensively. A recent report 4 uncovers unsuspected roles of Cdk1 kinase in the recovery from SAC-induced mitotic arrest. This study in yeast shows that cells attempting to recover

This is an important study on the damage-induced checkpoint maintenance and termination in budding yeast that provides novel and convincing evidence for a role of the spindle assembly checkpoint and mitotic exit network in halting the cell cycle after prolonged arrest in response to irreparable DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). The study identifies particular components from these checkpoints

Mitotic entry: The interplay between Cdk1, Plk1 and Bora Biology Diagrams
Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) is an important mitotic kinase that is crucial for entry into mitosis after recovery from DNA damage-induced cell cycle arrest. Plk1 activation is promoted by the conserved protein Bora (SPAT-1 in C. elegans), which stimulates the phosphorylation of a conserved residue in the activation loop by the Aurora A kinase. A surveillance mechanism known as the mitotic checkpoint supervises the process of chromosome segregation and arrests cell cycle progression when the cells were treated with 3 μg/ml α-factor for 2 hours. To induce mitotic arrest, cells were treated with 15 μg/ml of nocodazole (from a 100X stock in DMSO). In experiments with prolonged