Catch and release how do kinetochores hook the right microtubules Biology Diagrams Kinetochores are dynamic complexes containing MT motor and cell-cycle regulatory proteins, which serve three functions during cell division. They attach each replicated chromosome to the opposing poles of the mitotic spindle, help position the chromosome on the spindle and then inhibit chromatid separation (and anaphase onset) until all of the

Abstract The kinetochore is the multiprotein complex of eukaryotic organisms that is assembled on mitotic or meiotic centromeres to connect centromeric DNA with microtubules. Its function involves the coordinated action of more than 100 different proteins. The kinetochore acts as an organiser hub that establishes physical connections with microtubules and centromere-associated proteins and

A Molecular View of Kinetochore Assembly and Function Biology Diagrams
Abstract A critical requirement for mitosis is the distribution of genetic material to the two daughter cells. The central player in this process is the macromolecular kinetochore structure, which binds to both chromosomal DNA and spindle microtubule polymers to direct chromosome alignment and segregation. This review will discuss the key kinetochore activities required for mitotic chromosome
Kinetochore proteins can be grouped according to their concentration at kinetochores during mitosis: some proteins remain bound throughout cell division, whereas some others change in concentration. Furthermore, they can be recycled in their binding site on kinetochores either slowly (they are rather stable) or rapidly (dynamic).
The Kinetochore Biology Diagrams
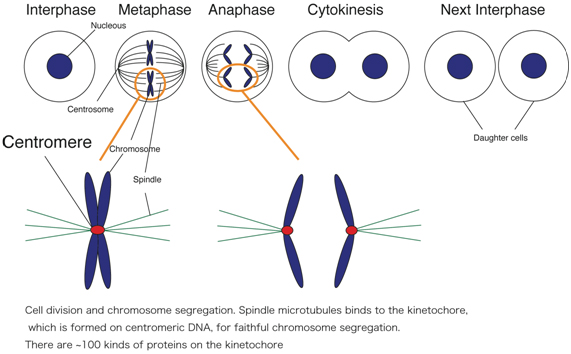
In mitosis, chromosomes condense and the two copies become visible as "sister chromatids". One kinetochore is assembled on each of the two sister chromatids of a chromosome, and both sister kinetochores become attached to opposite spindle poles by metaphase. During mitosis, it's up to the kinetochores assembled on the centromeres of each chromosome to give a cell the go-ahead to begin anaphase. A kinetochore will only give its ready signal once it becomes attached to and stretched apart by microtubules emanating from both opposing spindle poles. This process, known as the spindle checkpoint, ensures the even distribution of chromosomes between
